stroke
Defines how to draw a line.
A stroke has a paint (a solid color or gradient), a thickness, a line cap, a line join, a miter limit, and a dash pattern. All of these values are optional and have sensible defaults.
Example
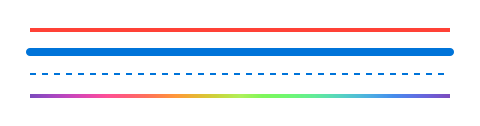
#set line(length: 100%)
#stack(
spacing: 1em,
line(stroke: 2pt + red),
line(stroke: (paint: blue, thickness: 4pt, cap: "round")),
line(stroke: (paint: blue, thickness: 1pt, dash: "dashed")),
line(stroke: 2pt + gradient.linear(..color.map.rainbow)),
)
Simple strokes
You can create a simple solid stroke from a color, a thickness, or a combination of the two. Specifically, wherever a stroke is expected you can pass any of the following values:
- A length specifying the stroke's thickness. The color is inherited, defaulting to black.
- A color to use for the stroke. The thickness is inherited, defaulting to
1pt. - A stroke combined from color and thickness using the
+operator as in2pt + red.
For full control, you can also provide a dictionary or a
stroke object to any function that expects a stroke. The dictionary's
keys may include any of the parameters for the constructor function, shown
below.
Fields
On a stroke object, you can access any of the fields listed in the
constructor function. For example, (2pt + blue).thickness is 2pt.
Meanwhile, stroke(red).cap is auto because it's unspecified. Fields
set to auto are inherited.
构造函数
如果类型具有构造函数,可以像函数一样调用它来创建一个该类型的值。
Converts a value to a stroke or constructs a stroke with the given parameters.
Note that in most cases you do not need to convert values to strokes in order to use them, as they will be converted automatically. However, this constructor can be useful to ensure a value has all the fields of a stroke.
#let my-func(x) = {
x = stroke(x) // Convert to a stroke
[Stroke has thickness #x.thickness.]
}
#my-func(3pt) \
#my-func(red) \
#my-func(stroke(cap: "round", thickness: 1pt))

paint
The color or gradient to use for the stroke.
If set to auto, the value is inherited, defaulting to black.
thickness
The stroke's thickness.
If set to auto, the value is inherited, defaulting to 1pt.
cap
How the ends of the stroke are rendered.
If set to auto, the value is inherited, defaulting to "butt".
-
"butt"Square stroke cap with the edge at the stroke's end point.
-
"round"Circular stroke cap centered at the stroke's end point.
-
"square"Square stroke cap centered at the stroke's end point.
join
How sharp turns are rendered.
If set to auto, the value is inherited, defaulting to "miter".
-
"miter"Segments are joined with sharp edges. Sharp bends exceeding the miter limit are bevelled instead.
-
"round"Segments are joined with circular corners.
-
"bevel"Segments are joined with a bevel (a straight edge connecting the butts of the joined segments).
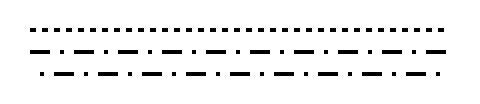
dash
The dash pattern to use. This can be:
- One of the predefined patterns:
"solid"ornone"dotted""densely-dotted""loosely-dotted""dashed""densely-dashed""loosely-dashed""dash-dotted""densely-dash-dotted""loosely-dash-dotted"
- An array with alternating lengths for dashes and gaps. You can
also use the string
"dot"for a length equal to the line thickness. - A dictionary with the keys
array(same as the array above), andphase(of type length), which defines where in the pattern to start drawing.
If set to auto, the value is inherited, defaulting to none.
-
"solid" -
"dotted" -
"densely-dotted" -
"loosely-dotted" -
"dashed" -
"densely-dashed" -
"loosely-dashed" -
"dash-dotted" -
"densely-dash-dotted" -
"loosely-dash-dotted"
 查看示例
查看示例
#set line(length: 100%, stroke: 2pt)
#stack(
spacing: 1em,
line(stroke: (dash: "dashed")),
line(stroke: (dash: (10pt, 5pt, "dot", 5pt))),
line(stroke: (dash: (array: (10pt, 5pt, "dot", 5pt), phase: 10pt))),
)
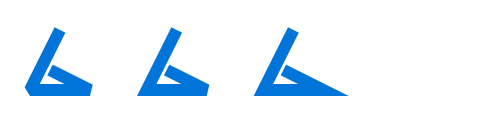
miter-limit
Number at which protruding sharp bends are rendered with a bevel
instead or a miter join. The higher the number, the sharper an angle
can be before it is bevelled. Only applicable if join is
"miter".
Specifically, the miter limit is the maximum ratio between the corner's protrusion length and the stroke's thickness.
If set to auto, the value is inherited, defaulting to 4.0.
 查看示例
查看示例
#let points = ((15pt, 0pt), (0pt, 30pt), (30pt, 30pt), (10pt, 20pt))
#set path(stroke: 6pt + blue)
#stack(
dir: ltr,
spacing: 1cm,
path(stroke: (miter-limit: 1), ..points),
path(stroke: (miter-limit: 4), ..points),
path(stroke: (miter-limit: 5), ..points),
)