arguments
Captured arguments to a function.
Argument Sinks
Like built-in functions, custom functions can also take a variable number of
arguments. You can specify an argument sink which collects all excess
arguments as ..sink. The resulting sink value is of the arguments
type. It exposes methods to access the positional and named arguments.
#let format(title, ..authors) = {
let by = authors
.pos()
.join(", ", last: " and ")
[*#title* \ _Written by #by;_]
}
#format("ArtosFlow", "Jane", "Joe")
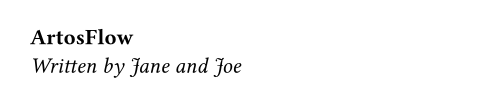
Spreading
Inversely to an argument sink, you can spread arguments, arrays and
dictionaries into a function call with the ..spread operator:
#let array = (2, 3, 5)
#calc.min(..array)
#let dict = (fill: blue)
#text(..dict)[Hello]

构造函数
如果类型具有构造函数,可以像函数一样调用它来创建一个该类型的值。
如果类型具有构造函数,可以像函数一样调用它来创建一个该类型的值。
Construct spreadable arguments in place.
This function behaves like let args(..sink) = sink.
#let args = arguments(stroke: red, inset: 1em, [Body])
#box(..args)

arguments
The arguments to construct.
定义
函数和类型可以有与其关联的定义 (成员或方法)。可以使用 "." 操作符来访问调用它们。
函数和类型可以有与其关联的定义 (成员或方法)。可以使用 "." 操作符来访问调用它们。
pos
Returns the captured positional arguments as an array.
self.pos() -> array
named
Returns the captured named arguments as a dictionary.
self.named() -> dictionary